FiveFrameSwing
Banned
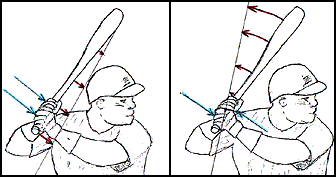
The actions at barrel-transition are critical to the building of a good swing.
You can not efficiently apply torque while thrusting the top hand forward. Shoving both hands forward will only accelerate the bat length-wise ... knob first.
To apply torque, the top hand must pull in a direction orthogonal to the length of the bat.
You can not efficiently apply torque while thrusting the top hand forward. Shoving both hands forward will only accelerate the bat length-wise ... knob first.
To apply torque, the top hand must pull in a direction orthogonal to the length of the bat.